Key Takeaways for Kimi-K2.5
- Kimi-K2.5 boasts an industry-leading 200,000-token context window, ideal for comprehensive long-form document processing and analysis.
- Setting up requires Python 3.9+, specific PyTorch and `transformers` versions, and significant NVIDIA GPU VRAM (40GB+ recommended).
- Optimize inference with BFloat16 for memory and speed, and FlashAttention-2 for enhanced attention mechanism efficiency.
- Troubleshoot common issues like Out-of-Memory (OOM) errors by utilizing quantization (4-bit/8-bit) and verifying GPU compatibility.
- Be aware of Kimi-K2.5's language bias (Qwen1.5-7B-Chat base) and its specialization in context length over raw general reasoning power.
Mastering Kimi-K2.5: Your Guide to 200K Context Window AI
Kimi-K2.5, a powerful large language model from Moonshot AI, introduces a significant advancement in how we handle extensive data with AI.
Its core strength lies in an impressive 200,000-token context window, making it an indispensable tool for tasks involving extremely long documents and complex reasoning.
This guide will walk you through setting up, using, and optimizing Kimi-K2.5 for your production-ready applications, sharing practical insights gained from real-world usage.
Kimi-K2.5's 200K Context Window: Mastering Long-Form AI
The most impactful feature of Kimi-K2.5 is its substantial 200,000-token context window.
While many models operate within 32K or 128K token limits, Kimi-K2.5's capacity fundamentally shifts how you can leverage AI for sophisticated, long-form tasks.
This extensive context means the model can process and retain information from approximately 150,000 words in a single prompt.
Think of it as providing an entire novel, a comprehensive legal brief, or a large software project's complete codebase at once.
This capability offers distinct advantages:
- Lossless Summarization:
Summarize lengthy research papers or detailed financial reports without missing crucial early details.
- Complex Document Analysis:
Pose intricate questions about an extensive legal contract or a detailed technical manual, and the model can synthesize information from across multiple sections simultaneously.
- Coherent Long-Form Generation:
Generate entire chapters, scripts, or comprehensive technical documentation, maintaining consistent characters, plot points, and terminology throughout. - Codebase Understanding:
Feed an entire application's source code to the model to inquire about functionality, pinpoint bugs, or generate documentation effortlessly.

The following table highlights how Kimi-K2.5 stands apart in context handling:
| Feature | Small Context Models (Pre-2024) | Large Context Models (2025-2026) | Kimi-K2.5 (200K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Context Size | 4K - 16K tokens | 32K - 128K tokens | 200K tokens |
| Use Case | Chatbots, short Q&A, simple summarization | Multi-document Q&A, code module analysis | Full codebase analysis, novel-length content generation, legal case review |
| Limitation | Prone to 'forgetting' early parts of a conversation or document. | Requires chunking for very large documents. | Can handle most single documents or small codebases in one go. |
Setting Up Your Environment for Kimi-K2.5: Dependencies and Hardware Essentials
To run Kimi-K2.5 effectively, a properly configured environment is critical.
As of early 2026, standard machine learning toolchains are mature, but specific hardware remains essential for optimal performance.
1. Python Environment
Ensure you have Python 3.9 or newer installed.
It's always a good practice to use a virtual environment to manage dependencies.
python -m venv kimi_env
source kimi_env/bin/activate # On Linux/macOS
# .\kimi_env\Scripts\activate # On Windows
2. Install Core Libraries
Install PyTorch, `transformers`, and Accelerate.
For GPU support, ensure you install the CUDA-enabled version of PyTorch.
pip install torch transformers accelerate
# Recommended: Install libraries for optimization
pip install bitsandbytes # For quantization
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation # For FlashAttention2
3. Hardware & CUDA Configuration
- GPU:
An NVIDIA GPU is required.
For optimal performance with BFloat16 and FlashAttention2, an Ampere-series card (e.g., A100, RTX 3090) or newer (e.g., Hopper, Blackwell series) is necessary.
- VRAM:
For the full 200K context, a significant amount of VRAM is needed.
Even with optimization, expect to need at least 40GB of VRAM.
For smaller context tasks or with heavy quantization, consumer cards with 24GB may suffice. - CUDA:
Verify your NVIDIA driver and CUDA toolkit are up to date.
CUDA 12.1+ is the standard in 2026.
You can check your CUDA version using `nvidia-smi` in your terminal.

Your First Kimi-K2.5 Text Generation: From Basic Prompts to Advanced Control
Getting started with Kimi-K2.5 is straightforward using the Hugging Face `transformers` library.
Your First Generation ('Hello World')
This code snippet loads the model and tokenizer, then runs a simple text generation task.
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
device = "cuda" # Ensure you have a CUDA-enabled GPU
# Load the tokenizer and model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
"moonshotai/Kimi-K2.5",
trust_remote_code=True
)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"moonshotai/Kimi-K2.5",
trust_remote_code=True,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="auto"
)
# Prepare your input text
text = "Kimi is a large language model from"
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": text}
]
# Generate text
input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, add_generation_prompt=True, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
gen_tokens = model.generate(
input_ids,
max_new_tokens=100,
do_sample=True
)
gen_text = tokenizer.decode(gen_tokens[0])
print(gen_text)
Advanced Control Parameters
To fine-tune the output for your specific application, consider these generation parameters:
- `temperature` (e.g., `0.8`):
This parameter controls the randomness of the output.
Higher values (around `1.0`) encourage more creative and diverse responses, while lower values (around `0.2`) produce more deterministic and focused text.
- `top_p` (Nucleus Sampling) (e.g., `0.9`):
This is a more advanced method to manage randomness.
It restricts the model to consider only the most probable tokens whose cumulative probability reaches the `top_p` threshold, helping to avoid incoherent generations. - `max_new_tokens` (e.g., `512`):
Use this to set the maximum length of the generated text.
It's crucial for preventing excessively long or "runaway" generations.
Troubleshooting Kimi-K2.5: Common Issues and Resolutions
Working with large language models often involves encountering and resolving common issues.
Here are some you might face with Kimi-K2.5:
- `Trust Remote Code` Warning:
You will see a prompt asking you to trust remote code.
This occurs because Kimi-K2.5 uses a custom model architecture not yet fully integrated into the standard `transformers` library.
You must pass `trust_remote_code=True` to load it.
Always ensure you are loading models from trusted sources, such as Moonshot AI's official Hugging Face repository.
- Out-of-Memory (OOM) Errors:
The `device_map='auto'` setting can sometimes allocate memory inefficiently, leading to OOM errors, especially with the 200K context.
If this happens, consider using quantization (`load_in_4bit=True`) to significantly reduce VRAM usage.
Alternatively, if you have a multi-GPU setup, you might need to manually assign model layers to specific devices for better control.
- `transformers` Version Conflicts:
As of early 2026, ensure you are using a recent version of `transformers` (e.g., 4.35.0 or newer).
Older versions may lack support for Kimi-K2.5's architecture or essential optimizations like FlashAttention-2. - BFloat16/FlashAttention2 Not Enabled:
If you observe errors or suboptimal performance, verify these points:- Your GPU supports BFloat16 (Ampere architecture or newer NVIDIA cards).
- You have successfully installed the `flash-attn` library (`pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation`).
- You are passing both `torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16` and `attn_implementation="flash_attention_2"` when loading the model.

Optimizing Kimi-K2.5 Inference: Leveraging BFloat16 and FlashAttention-2
For any serious application, optimizing inference speed and memory footprint is crucial.
Kimi-K2.5, with its vast context window, particularly benefits from these techniques.
- BFloat16 (`torch.bfloat16`):
This 16-bit floating-point format offers a significant advantage.
It effectively halves the model's memory footprint compared to standard 32-bit precision (FP32) while preserving the dynamic range of FP32, resulting in minimal impact on accuracy.
Enable it by passing `torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16` during model loading. - FlashAttention-2:
This is a highly efficient implementation of the attention mechanism.
It dramatically speeds up computation, especially for long sequences, by intelligently restructuring the attention calculations to minimize slow memory reads and writes from the GPU's High Bandwidth Memory (HBM).
Enable it with `attn_implementation="flash_attention_2"`.
Optimized Loading Snippet
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"moonshotai/Kimi-K2.5",
trust_remote_code=True,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, # Use bfloat16 for speed and memory
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2", # Use FlashAttention-2
device_map="auto"
)
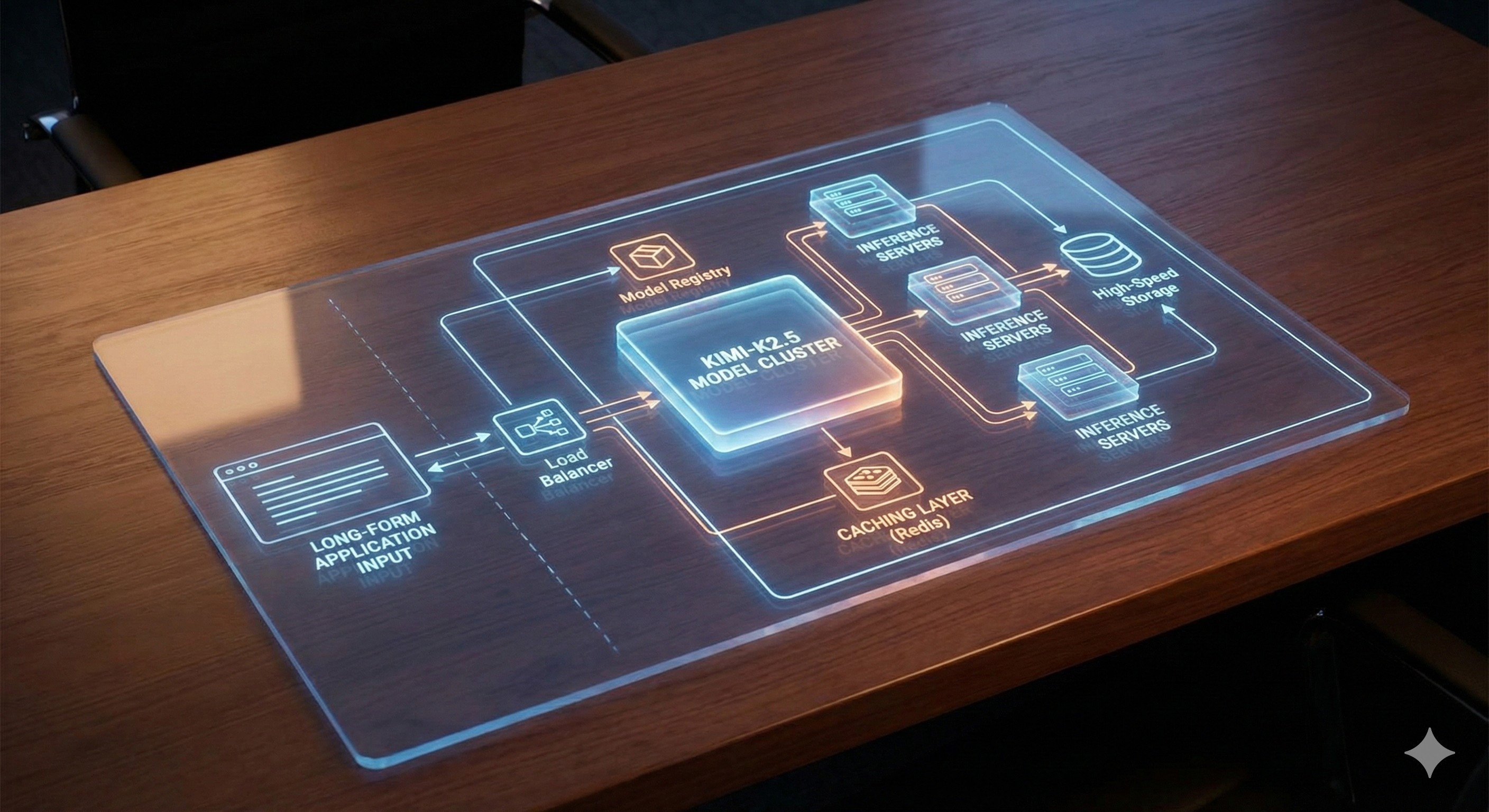
Deploying Kimi-K2.5 for Production: Best Practices for Long-Form AI Applications
Deploying a model with a 200K context window introduces unique challenges that require careful planning.
- Manage Latency:
A single request with a 200K token prompt will inherently be slow.
Design your application to handle this asynchronously.
Utilize streaming APIs to return tokens as they are generated, which significantly improves the user experience.
- Use Specialized Inference Servers:
Leverage tools designed for high-throughput, low-latency LLM serving.
Solutions like vLLM, TensorRT-LLM, or Hugging Face's Text Generation Inference (TGI) incorporate advanced techniques such as paged attention to efficiently manage memory for long contexts.
- Implement Smart Caching:
For applications where similar, extensive documents are processed repeatedly, a caching layer is invaluable.
Store results to avoid redundant, expensive computations and generations. - Cost and Resource Planning:
Running a model with such a large context window is resource-intensive.
Carefully plan your GPU infrastructure and associated costs.
Consider using spot instances or serverless GPU platforms where feasible to manage expenses.
Kimi-K2.5's Strengths and Limitations: Focus on Language and Bias
Understanding any tool's capabilities and constraints is key to effective use.
- Primary Strength:
Kimi-K2.5 offers unparalleled long-context processing capability.
It is specifically built for tasks that demand a holistic understanding of extensive texts, making it excellent for deep analysis and synthesis.
- Primary Limitation (Language & Bias):
Kimi-K2.5 is based on `Qwen1.5-7B-Chat`, a model trained on a large corpus that includes a significant portion of Chinese data.
While it performs well in English, its fluency, cultural nuance, and safety alignment might be stronger in Chinese contexts.
Developers should be aware of potential biases stemming from its training data and rigorously test it for applications involving sensitive or non-Chinese cultural contexts. - Model Size: As a 7-billion parameter model, its general reasoning capabilities may not match those of much larger models (e.g., 70B+ parameter models).
Its specialization clearly lies in its exceptional context length, rather than raw, broad reasoning power.

Memory Management for Kimi-K2.5: Strategies for Large Contexts
Effectively managing VRAM is often the largest hurdle when working with a model like Kimi-K2.5.
Quantization: This is the most effective technique for reducing memory footprint.
By loading the model with lower-precision weights, you can drastically cut its VRAM requirements.
- 8-bit:
Loading with `load_in_8bit=True` provides a good balance between performance and memory savings. - 4-bit:
`load_in_4bit=True` offers maximum memory savings, potentially allowing you to run the model on consumer GPUs, though typically with a minor impact on output quality.
This method requires the `bitsandbytes` library to be installed.
# Example of 4-bit loading
from transformers import BitsAndBytesConfig
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"moonshotai/Kimi-K2.5",
trust_remote_code=True,
quantization_config=quantization_config,
device_map="auto"
)
Efficient Batching:
When conducting batch inference, ensure your batch sizes are carefully tuned to your hardware.
This maximizes throughput without triggering Out-of-Memory (OOM) errors.
Gradient Checkpointing:
During fine-tuning, this technique significantly saves memory by re-computing gradients during the backward pass rather than storing them throughout the entire process.
It trades a small amount of compute time for a considerably lower memory footprint.

Fine-tuning Kimi-K2.5: Adapting for Domain-Specific Tasks (Conceptual Guide)
Fine-tuning Kimi-K2.5 allows you to adapt its powerful capabilities to your specific domain, such as legal technology, biotech research, or a corporate knowledge base.
This is a conceptual overview of the process.
Conceptual Steps:
Curate a High-Quality Dataset:
Create a dataset of prompt-completion pairs highly specific to your target domain.
For Kimi-K2.5, it is essential to include many examples with long contexts to ensure its core strength is retained.
Choose a Fine-tuning Method:
- Full Fine-tuning:
This method retrains all model weights.
While resource-intensive, it can yield the best performance for highly specialized tasks. - Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT):
Methods like LoRA or QLoRA freeze the original model weights and train only small, additional 'adapter' layers.
This approach is significantly more memory-efficient and is the recommended starting point for most use cases.
Use a Training Framework:
Leverage established libraries such as Hugging Face's `trl` or `axolotl` to streamline the fine-tuning process.
Evaluate Rigorously:
Test the fine-tuned model on a separate validation set.
This is crucial to confirm that it has indeed improved on your specific task without suffering from 'catastrophic forgetting' of its general capabilities.

For further details and official documentation, you can refer to the model's page on the Hugging Face Hub and the official documentation for relevant libraries.
- Hugging Face Kimi-K2.5: https://huggingface.co/moonshotai/Kimi-K2.5
- PyTorch Documentation: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/index.html
moonshotai/Kimi-K2.5 · Hugging Face
We’re on a journey to advance and democratize artificial intelligence through open source and open science.
huggingface.co
PyTorch documentation — PyTorch 2.10 documentation
docs.pytorch.org



